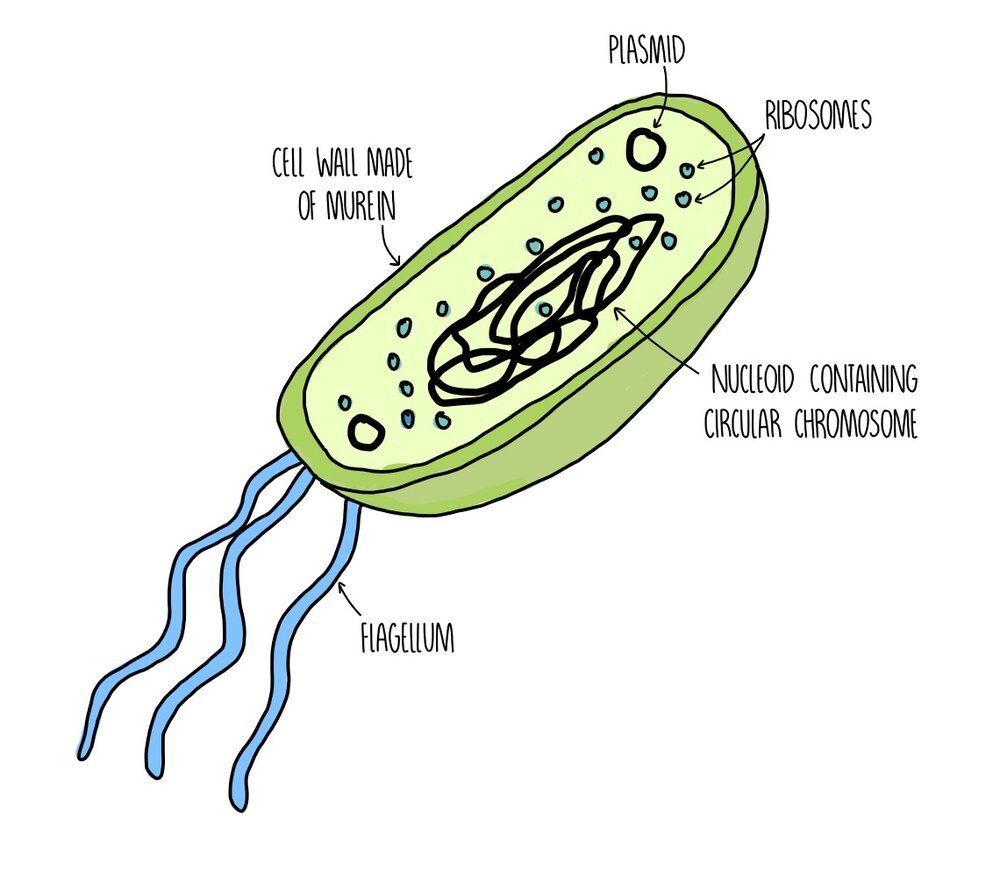
64 Prokaryotic Cell Division Concepts of Biology 1st Canadian Edition Biology Diagrams Typically, prokaryotic cell sizes range from 0.1 to 5.0 μm in diameter and thus are significantly smaller than eukaryotic cells. They have a surface area to volume ratio higher than eukaryotes because of their small size. Shapes. The three most common prokaryotic cell shapes are spiral (coiled-shaped), bacillus (rod-shaped), and coccus
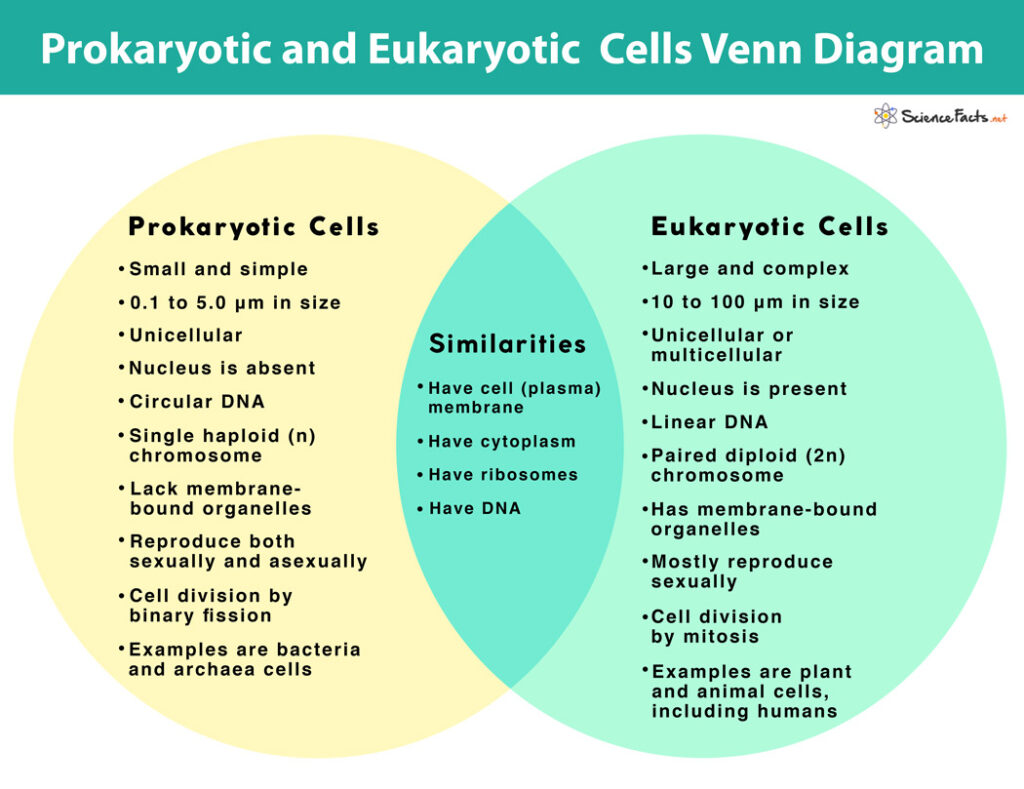
Structure of Prokaryotic Cells. The diagram of prokaryotic cells shows that it has a simple structure and lack complex organelles like mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, etc. The prokaryotic cells example are archae and bacteria. The structure of a prokaryotic cell is discussed below: Size of prokaryotic cells can vary betwween 0.1 -5.0 µm.

Prokaryotic Cell: Definition, Examples, & Structure Biology Diagrams
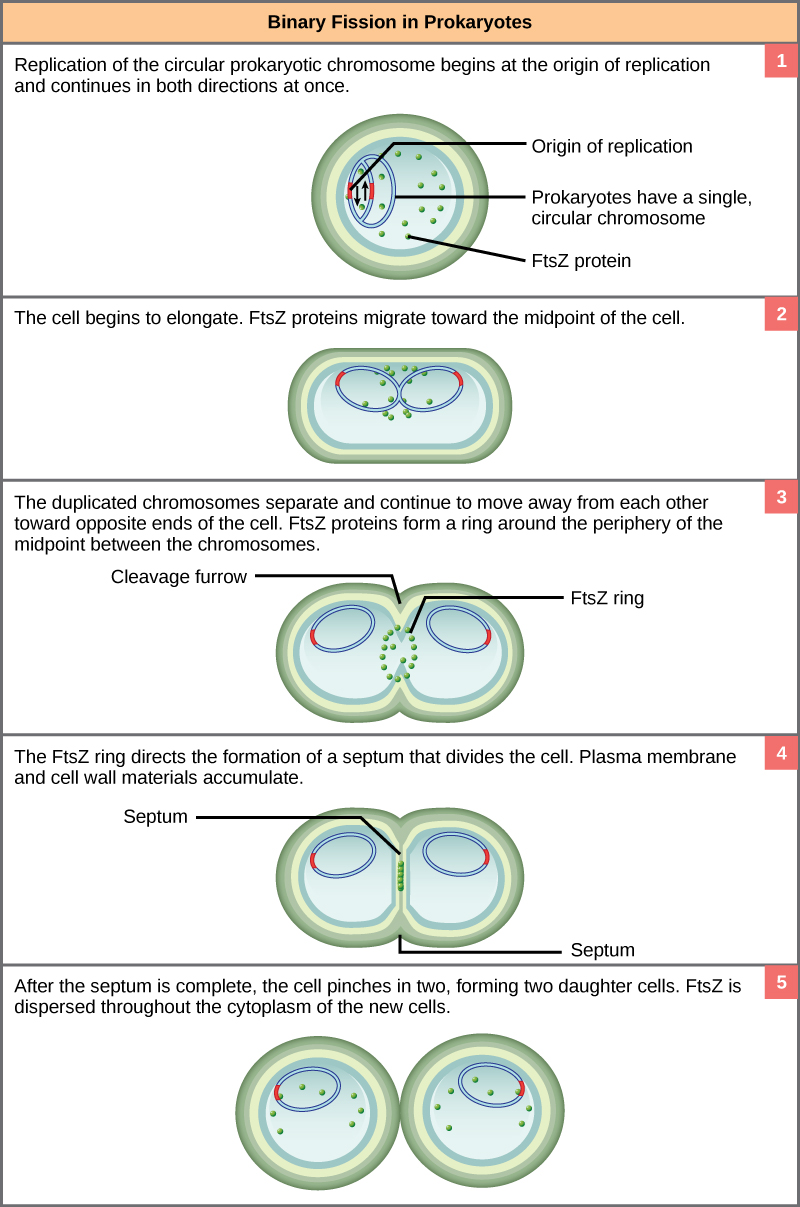
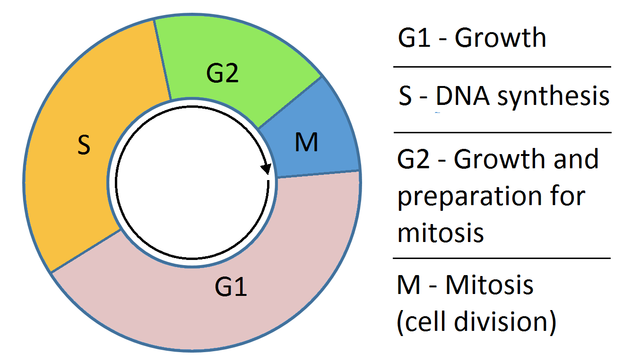
The following points highlight the four major phases of the cell cycle. The phases are: 1. G 1 (gap1) phase 2. S (synthesis) phase 3. G 2 (gap 2) phase 4. M (mitosis) phase. Cell Cycle: Phase # 1. G 1 Phase: . The G 1 phase is set in immediately after the cell division. It is characterised by a change in the chromosome from the condensed mitotic state to the more extended interphase state and The Components of a Typical Prokaryotic Cell. All prokaryotic cells have a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, nucleoid, and ribosomes. Other components vary by species. Cytoplasm. The cytoplasm is a gel-like substance inside the cell that surrounds all other cell components, like ribosomes and DNA. The cytoplasm is primarily water but also includes
Prokaryotic Cell Diagram. The following image is a diagram of a prokaryotic cell; in this case, a bacterium. The Anatomy of a Bacterial Cell Prokaryotic Cell Structure. Prokaryotic cells do not have a true nucleus that contains their genetic material as eukaryotic cells do. The cell cycle is the sequence of events occurring in an ordered fashion which results in cell growth and cell division. The overall process and steps of the cell cycle might differ in eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms as a result of the differences in their cell complexity. applications with diagram 6. Cytokinesis. Cytokinesis is
Cell Cycle: Definition, Phases, Regulation, Checkpoints Biology Diagrams
The prokaryotic cells have four main components: Plasma Membrane- It is an outer protective covering of phospholipid molecules which separates the cell from the surrounding environment. Cytoplasm- It is a jelly-like substance present inside the cell.All the cell organelles are suspended in it. DNA- It is the genetic material of the cell.All the prokaryotes possess a circular DNA. The G 0 phase is a "resting" phase where the cell exits the cell cycle and stops dividing. Some cells, like neurons and muscle cells, enter this phase semi-permanently and may never undergo division again. This phase is crucial for: Conserving energy and resources in non-dividing cells. Specializing cells for specific functions. Regulation