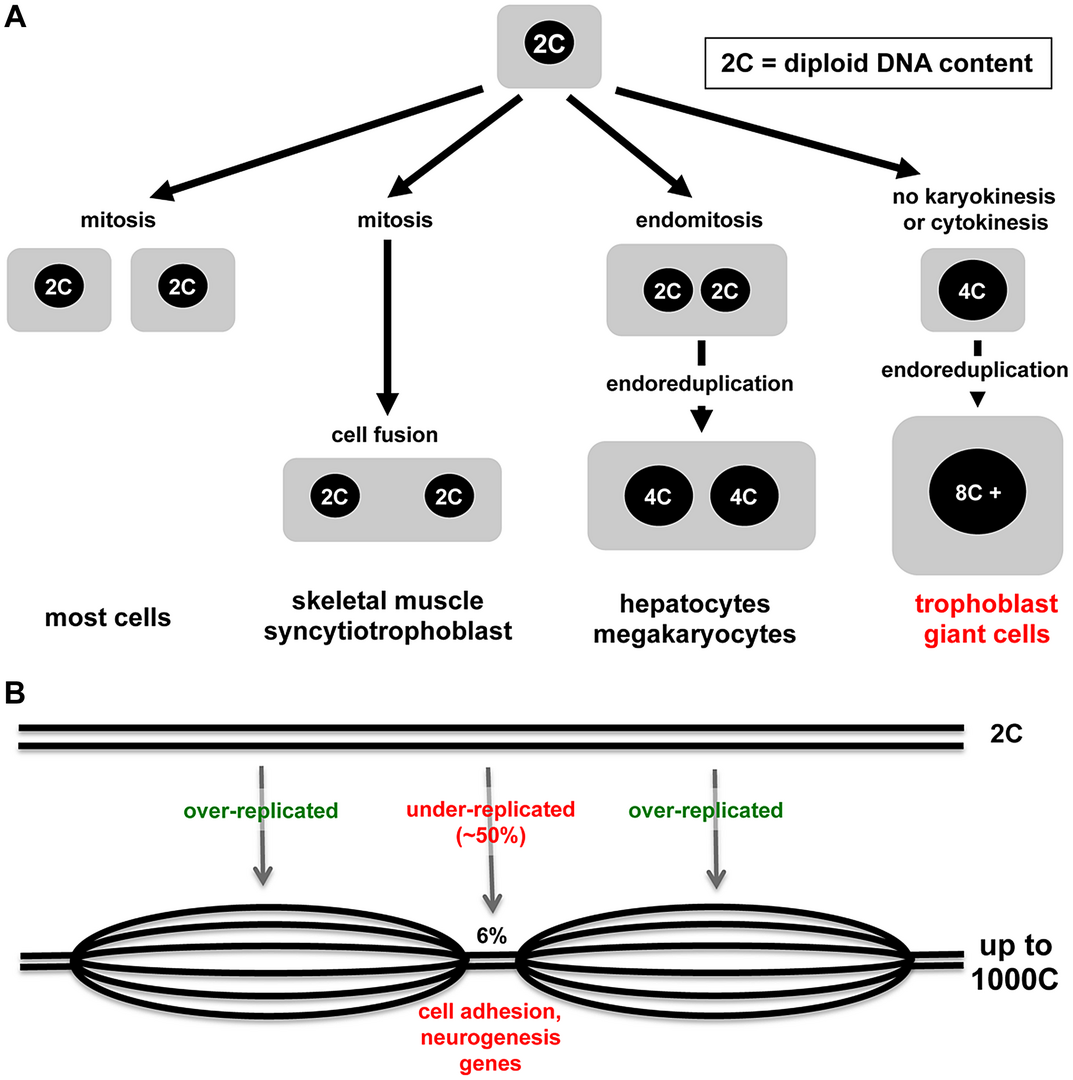
Figure 1 from A model describing cell polyploidization in tissues of Biology Diagrams Consequently, two important events must occur in order to convert a mitotic cycle into an endoreplication cycle and achieve polyploidy: (1) cell division must be suppressed; and (2) CDK activity must continue to alternate between low and high levels in order for the genome to be reduplicated in the absence of cell division. As we discuss below Polyploidy can arise at both the organismal and suborganismal levels. At the organismal level, unreduced gametes (e.g., diploid instead of haploid) formed during meiosis can fuse to generate whole-organism polyploidy. Organismal polyploidy is a major driver of biodiversity that extends across all life, from deep history to the recent past [1, 2].Most, if not all, extant species (including our

Cell Cycle Variants Yielding Polyploid Cells. (A) The archetypal cell cycle responsible for cell proliferation contains a G1 phase during which sufficient cell growth must occur prior to the onset of DNA replication in S phase. Another gap phase (G2) precedes mitosis and the return to G1 in the two daughter cells.
When Bigger Is Better: The Role of Polyploidy in Organogenesis Biology Diagrams
One use of polyploidy is to generate large cells, such as mammalian megakaryocytes or the giant cells that contribute to the structure of organs such as Arabidopsis leaves. It has been appreciated since late in the 19 th century that cell size is proportional to nuclear size, and this was subsequently shown to reflect DNA content. Thus, both polyploid and polytene cells are of increased size

In this context, neuronal cell cycle re-entry is widely considered to be aberrant and deleterious to neuronal health. In this review, we highlight historical and emerging reports of polyploidy in the nervous systems of various vertebrate and invertebrate organisms.

entry in the Nervous System: From Polyploidy to ... Biology Diagrams
The resulting cell is polyploid in DNA content. There are different types of endoreplication cycles, and different contexts in which cells employ them to become polyploid. Endoreplication cycles utilize parts of the cell cycle machinery to replicate DNA, but these cycles are curtailed and result in one cell with increased DNA content instead